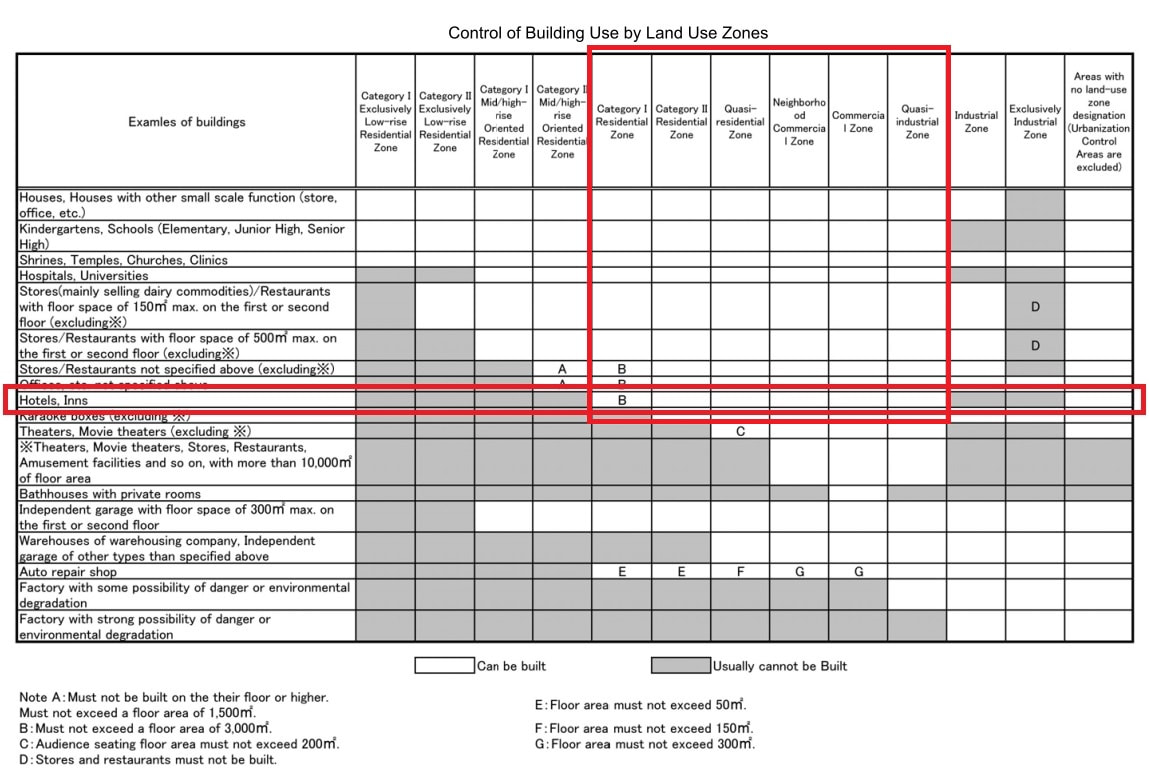
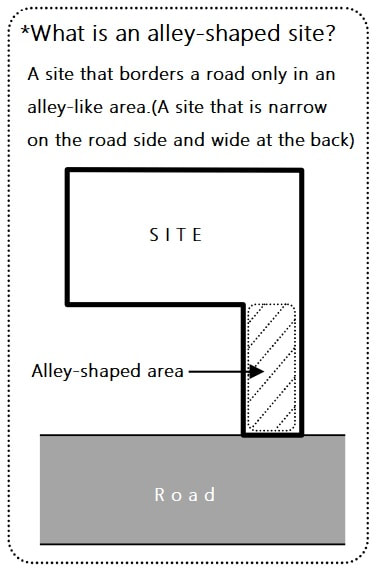
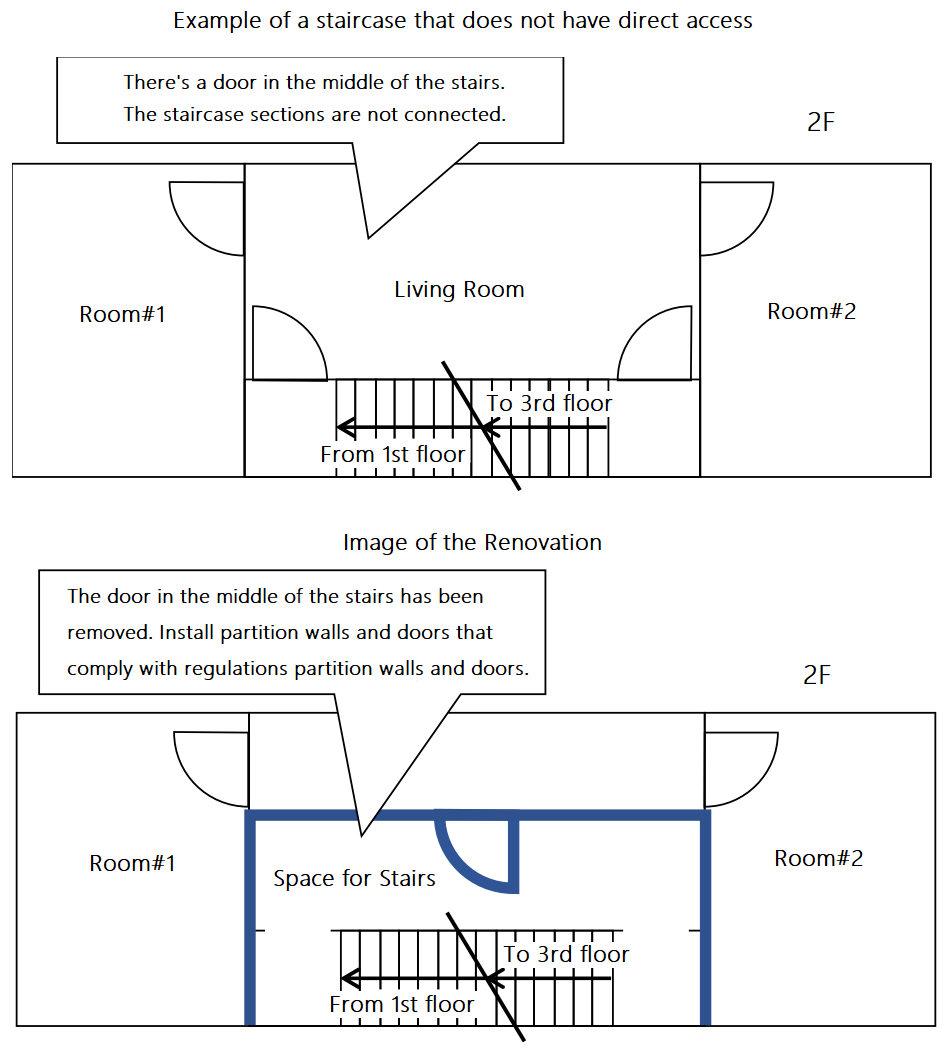
Major provisions of the Building Standards Act applicable to accommodation facilities under the Hotel Business LawFor those who are planning to open an accommodation facility based on the Ryokan Business Act In order to operate a lodging facility (hotel, inn, guesthouse, etc.) based on the Ryokan Business Act, the building in which the business is planned to be conducted must meet the structural and equipment standards stipulated in the Ryokan Business Act and the Fire Service Act. The Building Standards Act stipulates the zoning districts in which lodging facilities (including entrance halls outside facilities) can operate. Kyoto city ask that you confirm the zoning of the property before considering it, as follows. < Regulations Other than Zoning > When changing the use of an existing building and using it as a lodging facility, even if no building permit is required (e.g., area less than 200m², not involving expansion, renovation, or major repair or redecoration), it is necessary to comply with various provisions of the Building Standards Act. Please refer to the following main provisions of the Building Standards Act for the details of the regulations. In addition, before using the facility as a lodging facility, it is necessary to complete the necessary procedures based on the Barrier Free Ordinance. Major provisions of the Building Standards Act applicable to accommodation facilities under the Hotel Business Law - As a general rule, buildings on alley-shaped site* (see explanation below) cannot be changed to inns. - If the existing building does not conform to the provisions of the Building Standard Act, it is necessary to change the use of the building after the illegal part is removed. - In principle, the building must be fireproof when changing the use of the third floor or more to an inn. Even if the building is not a fireproof building (limited to 3 stories and less than 200m² in total area), it is necessary to install a pit compartment and alarm system. *An automatic fire alarm system or an automatic fire alarm system for specified small facilities with a receiver is required. This is not a residential fire alarm system. **Linen rooms and employee offices are also "ryokan uses". - If there is fire use, ventilation equipment must be installed. - Emergency lighting must be installed. - The site passage (passage from the exit of the building to the road, etc.) must be 1.5m or more (From April 2020, 0.9m or more for buildings with 3 or less floors and a total floor area of less than 200m²). - The width of alleys, etc. must be at least 1.5m regardless of the size of the building, as in the past, for buildings to be used as accommodation facilities in accordance with the provisions of 9-67 of the Kyoto City Building Law Handbook. - For rooms without windows, the walls, etc. that separate the rooms must be made of fireproof or noncombustible materials. * In addition to guest rooms, rest rooms and kitchens are also "rooms". - In the case of a change of use of a row of buildings (attached houses) to an inn (including a partial change of use), the boundary wall between the row of buildings and the inn shall be a partition wall for fire prevention. It is necessary to use a wall of quasi-fireproof construction and compartmentalize it to the shed or ceiling. - In addition, depending on the floor area and other factors, it may be necessary to install two or more direct staircases, smoke exhaustion equipment, interior restrictions, etc. - If the building is to be expanded, remodeled, repaired, or redecorated, it must also comply with road access and structural regulations. - There are cases where procedures based on the Building Standards Act are required even when only renovations are to be done. Confirming whether or not a building complies with the Building Standards Act requires specialized knowledge. Even if you do not need to apply for a building permit, , if necessary, please consult with an architect or other professional to ensure that your plans and construction are carried out legally. The responsibility for using a building in violation of the law lies with the construction client (business) or building owner. Supplement for those who are planning to open an accommodation facility based on the Ryokan Business Act For inns with three floors and a total area of less than 200 m². 1 Overview With the enforcement of the revised Building Standards Act in June 2019, buildings with three floors and a total floor area of less than 200m² can be used as inns, etc., without having to be fireproof buildings, provided that alarm systems and certain compartments are installed. 2 Precautions (*Please be sure to check the following. In the case of a change of use of 200m² or less (not involving expansion, renovation, or large-scale repair), no application for building certification is required. However, due to the change of use, the provisions of the Building Standards Act will apply, and it will be necessary to comply with various regulations. Specialized knowledge is required to investigate whether or not these buildings comply with the Building Standards Act. Even if you do not need to apply for a building permit, please be sure to consult with an architect or other specialist before legally carrying out any planning or construction work. The responsibility for using a building in violation of the law lies with the construction client (business) or building owner. 3 Necessary actions (1) Alarm system An automatic fire alarm system or an automatic fire alarm system for specified small facilities with a receiver is required. This is not a residential fire alarm system. (2) Pit compartment a. Overview The stairs and other parts of the building must be separated by partition walls and doors. b. Form of stairs The staircase must be a "direct staircase" and the stairs from the third floor to the first floor must be connected without interruption. It is not possible to pass through the living room on the way, nor is it possible to have a door. c. "Partition walls" and "Doors" The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) gives the following examples in their explanation Partition walls: Partition walls with plasterboard of 9.5 mm or more in thickness on both sides Door: Flush door (with self-closing mechanism and smoke blocking performance, etc.) * You cannot use fusuma, shoji, walls made of plywood of about 3 mm thick, or doors made of plain glass. Examples of non-direct staircases and their responses
Comments are closed.
|
Details
AuthorArrows International Realty Corp. Archives
June 2023
Categories
All
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed