7-1 Financial Planning and Mortgage
Types of Mortgage Loans
When you take out a mortgage loan, you will be making repayments over a long period of time. There are various types of mortgage products, and the applicable interest rate and repayment amount will differ depending on which product you choose.
The following is a brief overview of how mortgage loans work and the features of each product in order to help you plan your finances appropriately.
When you take out a mortgage loan, you will be making repayments over a long period of time. There are various types of mortgage products, and the applicable interest rate and repayment amount will differ depending on which product you choose.
The following is a brief overview of how mortgage loans work and the features of each product in order to help you plan your finances appropriately.
Point 1: Know how interest rates work and their characteristics.
Check interest rates first.
The lower the interest rate, the lower the interest expense and the lower the total repayment amount. For example, if you borrow 10 million yen and make equal monthly repayments of principal and interest over 35 years, the difference in total repayments will be approximately 2.25 million yen if the interest rate is 3% or 2%.
Note that, in general, the interest rate on a mortgage loan is applied at the time of loan origination, not at the time of loan application. This means that there is a risk that the interest rate at the time of actual borrowing may be higher than the interest rate confirmed when you applied for the mortgage loan. In particular, when purchasing a newly built property for sale before it is completed, it is advisable to make a financial plan with sufficient time to consider the risk of interest rate increases since the loan will be executed after the property is completed.
The lower the interest rate, the lower the interest expense and the lower the total repayment amount. For example, if you borrow 10 million yen and make equal monthly repayments of principal and interest over 35 years, the difference in total repayments will be approximately 2.25 million yen if the interest rate is 3% or 2%.
Note that, in general, the interest rate on a mortgage loan is applied at the time of loan origination, not at the time of loan application. This means that there is a risk that the interest rate at the time of actual borrowing may be higher than the interest rate confirmed when you applied for the mortgage loan. In particular, when purchasing a newly built property for sale before it is completed, it is advisable to make a financial plan with sufficient time to consider the risk of interest rate increases since the loan will be executed after the property is completed.
Check the repayment method.
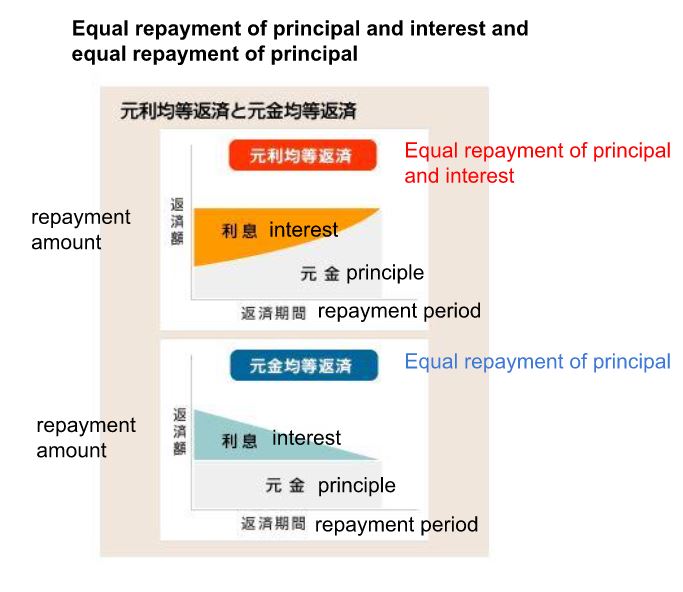
There are two main types of principal and interest repayment methods:
(1) equal repayment of principal and interest (a method in which the total amount of principal and interest to be repaid each time is set to be constant) and
(2) equal repayment of principal (a method in which the amount of principal to be repaid each time is set to be constant).
Equal repayment of principal and interest makes it easier to make a household budget schedule because the monthly repayment amount is fixed, but the pace of principal repayment is slower than with equal repayment of principal and interest, and if the loan term is the same, the total payment amount will be higher with equal repayment of principal and interest.
On the other hand, equal repayment of principal has the advantage of allowing the borrower to repay the principal amount faster, but the initial monthly repayment amount is higher. However, if the borrower is willing to make principal repayments quickly even if the initial repayment burden is heavier, it is advantageous to choose the equal principal repayment option.
Since many financial institutions only offer mortgages with equal repayment of principal and interest, it is advisable to check the mortgage products of each financial institution as early as possible when considering borrowing.
There are two main types of principal and interest repayment methods:
(1) equal repayment of principal and interest (a method in which the total amount of principal and interest to be repaid each time is set to be constant) and
(2) equal repayment of principal (a method in which the amount of principal to be repaid each time is set to be constant).
Equal repayment of principal and interest makes it easier to make a household budget schedule because the monthly repayment amount is fixed, but the pace of principal repayment is slower than with equal repayment of principal and interest, and if the loan term is the same, the total payment amount will be higher with equal repayment of principal and interest.
On the other hand, equal repayment of principal has the advantage of allowing the borrower to repay the principal amount faster, but the initial monthly repayment amount is higher. However, if the borrower is willing to make principal repayments quickly even if the initial repayment burden is heavier, it is advantageous to choose the equal principal repayment option.
Since many financial institutions only offer mortgages with equal repayment of principal and interest, it is advisable to check the mortgage products of each financial institution as early as possible when considering borrowing.
Point 2: Three main types of mortgage products
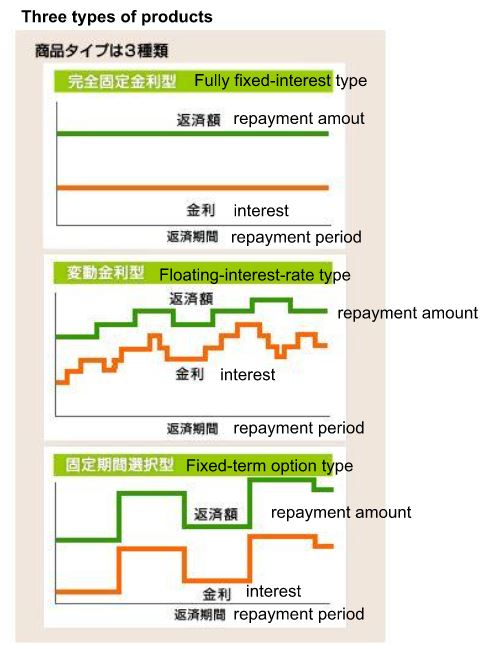
There are various product types, depending on how the interest rate is set relative to the principal. The three main types as follows.
(1) Fully fixed-interest-rate type
The fully fixed interest rate type is a product in which the interest rate is fixed for the entire loan period. Generally, if interest rates are expected to rise during the fixed interest rate period, the initial applicable interest rate will be higher than the variable interest rate type, etc. However, even if interest rates fluctuate during the borrowing period, the amount of mortgage loan repayment will not change from the initially set amount.
(2) Floating-interest-rate type
Floating-rate loans have interest rates that are reviewed semiannually, and the repayment amount is reviewed every five years based on interest rate movements. However, even if the repayment amount rises as interest rates fluctuate, it is capped at 1.25 times the existing repayment amount. In the event of a rise in interest rates, the initial applicable interest rate is generally lower than that of the fully fixed-rate type, but the borrower bears the risk of subsequent interest rate rises.
(3) Fixed-term option type
In the fixed-term option type, the interest rate is fixed for a certain period, such as 3 years or 5 years, and at the end of that period, the interest rate is set again (fixed term or variable interest rate) and the repayment amount is reviewed according to that interest rate. The choice of the fixed period varies from financial institution to financial institution. If the interest rate after the fixed period ends has risen significantly, the repayment amount may increase significantly because there is no upper limit to the amount of increase in the repayment amount as there is with the variable interest rate type.
The fully fixed interest rate type is a product in which the interest rate is fixed for the entire loan period. Generally, if interest rates are expected to rise during the fixed interest rate period, the initial applicable interest rate will be higher than the variable interest rate type, etc. However, even if interest rates fluctuate during the borrowing period, the amount of mortgage loan repayment will not change from the initially set amount.
(2) Floating-interest-rate type
Floating-rate loans have interest rates that are reviewed semiannually, and the repayment amount is reviewed every five years based on interest rate movements. However, even if the repayment amount rises as interest rates fluctuate, it is capped at 1.25 times the existing repayment amount. In the event of a rise in interest rates, the initial applicable interest rate is generally lower than that of the fully fixed-rate type, but the borrower bears the risk of subsequent interest rate rises.
(3) Fixed-term option type
In the fixed-term option type, the interest rate is fixed for a certain period, such as 3 years or 5 years, and at the end of that period, the interest rate is set again (fixed term or variable interest rate) and the repayment amount is reviewed according to that interest rate. The choice of the fixed period varies from financial institution to financial institution. If the interest rate after the fixed period ends has risen significantly, the repayment amount may increase significantly because there is no upper limit to the amount of increase in the repayment amount as there is with the variable interest rate type.
Other types of bank loans include those that combine multiple products and those with floating interest rates but with a maximum interest rate.
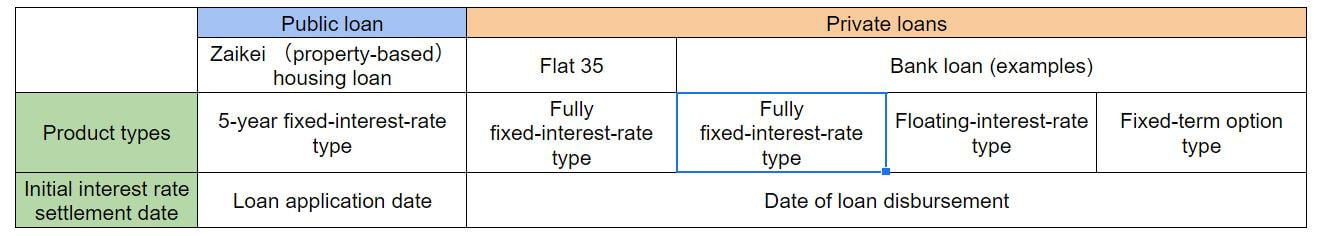
Note that the available product types may be limited depending on the mortgage loan. For Zaikei (property-based) housing loan, only the 5-year fixed-rate type, in which a fixed interest rate is applied for 5 years, is available, while Flat 35 (a mortgage loan provided by the Japan Housing Finance Agency in cooperation with private financial institutions) is only available in the fully fixed-rate type.
Note that the available product types may be limited depending on the mortgage loan. For Zaikei (property-based) housing loan, only the 5-year fixed-rate type, in which a fixed interest rate is applied for 5 years, is available, while Flat 35 (a mortgage loan provided by the Japan Housing Finance Agency in cooperation with private financial institutions) is only available in the fully fixed-rate type.
Major Mortgage Product Types